Difference between PWA Polishing Powder and WA Polishing Powder
PWA(plate shape calcined aluminum oxide) polishing powder and WA(White fused aluminum oxide) polishing powder are both excellent polishing powder. As a professional alumina polishing powder manufacturer, we woule like to explain the differences in detail below:
Item | PWA Polishing Powder | WA Polishing Powder |
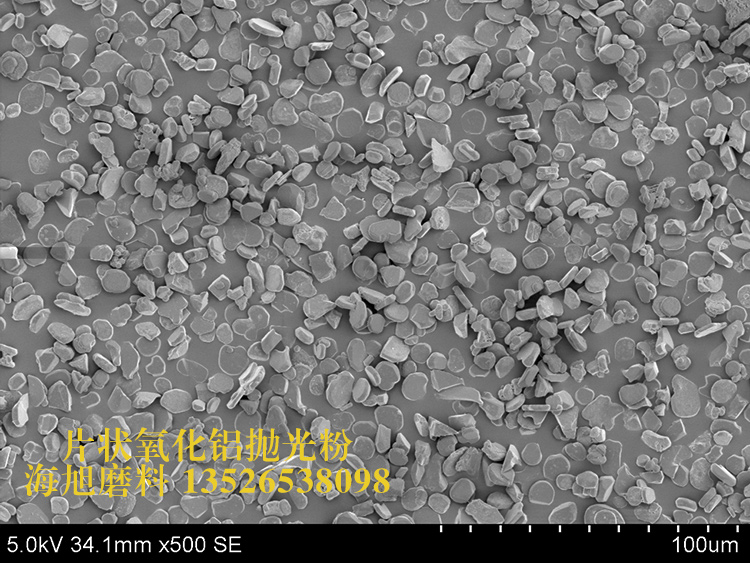
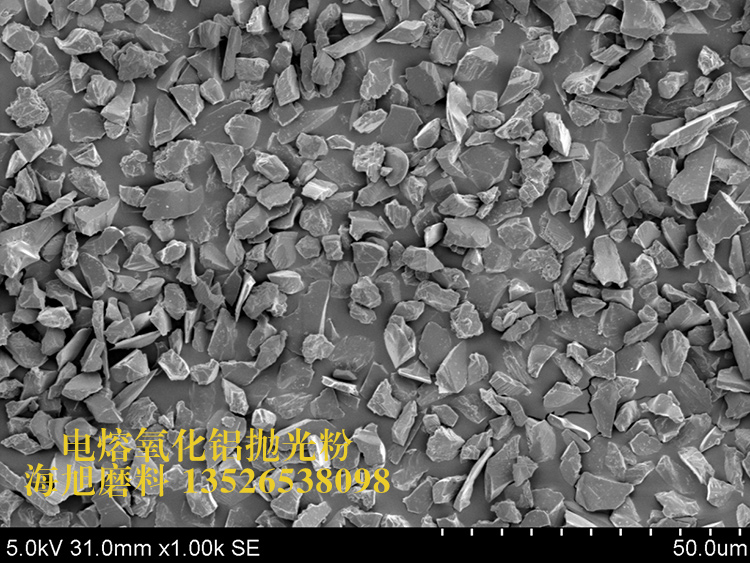
| Shape and appearance | Plate shape crystal(Platelet shape or tabulated shape) | Irregular, multi-faceted, fragmented, with sharp edge |
| Main Index | Al2O3 purity min. 99%,with the α-Al2O3 phase as the main crystalline phase, Mohs hardness close to 9.0. | Al2O3 purity min. 99% with high α-Al2O3 phase content, Mohs hardness 9.0 |
| Polishing function | Based on effective grinding, the PWA flat particles act on the workpiece surface in a planar sliding manner, avoiding polishing scratches. | WA particles etch the surface of the substrate, resulting in strong polishing force and high removal rate. |
| Manufacturing method | Alumina powder with additives is calcined in a rotary kiln at 1300℃ to produce a material in the form of plate shape crystals. Then milled, washed, precipitated, and sorted. | Alumina powder is smelted and refined in a high-temperature electric arc furnace at 2200℃, then cooled, crushed, and subsequently milleld, washed, precipitated, and sorted. |
| Particle size | The thickness of PWA polishing powder is fixed, and the diameter ranges from 3 to 50 μm. | A wide range of particle sizes are available, from 1µm to 63µm, to provide standard particle sizes. |
| Application | 1. Electronics Industry: Grinding and polishing of semiconductor single-crystal silicon wafers, CMP thinning of silicon wafers, piezoelectric quartz crystals, and compound semiconductors (gallium arsenide, indium phosphide).2. Glass Industry: Grinding and processing of crystal, quartz glass, cathode ray tube glass shells, optical glass, liquid crystal display (LCD) glass substrates, and piezoelectric quartz crystals.3. Coating Industry: Fillers for specialty coatings and plasma spraying.4. Metal and Ceramic Processing Industry: Precision ceramic materials, sintered ceramic raw materials, high-temperature coatings, etc. | 1. Wear-resistant fillers: Wear-resistant fillers for ceramic glazes, wood flooring wear layers, wear-resistant coatings, wear-resistant adhesives, polyurethane resins, plastic glass, composite brake pads, etc.2. Abrasives: Abrasives for materials such as cemented carbide, non-ferrous metals, stainless steel, alloy products, and soda-lime glass.3. Abrasive wheel raw materials: Main abrasives for oilstones, sandpaper, polishing wax, rubber grinding wheels, and grinding fluids, and auxiliary materials for diamond dry grinding discs.4. Ceramics: Ceramic films, insulating ceramic plates, honeycomb ceramics, etc. |
| Applicable equipment | Double-sided polishing and surface polishing equipment | Double-sided polishing, surface grinding, micro-blasting and sandblasting equipment |
| Impact on grinding & polishing equipment | The platelet structure has a smooth surface, resulting in low wear on equipment. | High hardness and multi-sharp-angled structures cause high wear on equipment. |